Gallbladder Surgery
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. The operation is usually done to remove the gallbladder due to gallstones causing pain or infection. There are also several other reasons to have gallbladder surgery. Your surgeon can discuss your specific case in detail during an office consultation. Cholecystectomy is one of the most common operations we perform.
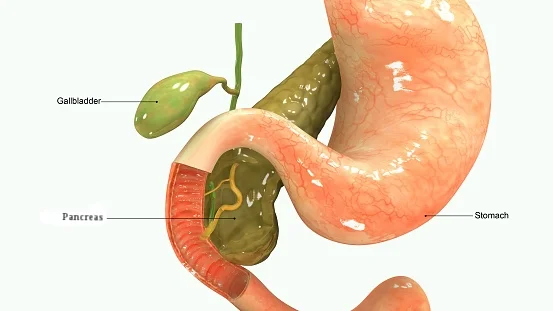
Gallbladder Basics:
The gallbladder is a small organ located in the right side of the abdomen under the liver. It is connected to the liver and intestines by small tubes called bile ducts. The main purpose of the gallbladder is to store a fluid called bile. Bile is a greenish-brown fluid that is made by the liver and helps your body absorb fatty foods and vitamins. After eating, the gallbladder squeezes bile into the intestines to help with digestion.
Some people form gallstones in the gallbladder. Gallstones form when cholesterol or bile in the gallbladder hardens. Over 1 million people in the United States are diagnosed with gallstones every year. In some cases, these gallstones can cause pain or other complications and must be treated. Gallstones are usually found by doctors using an ultrasound or a CT scan after you have symptoms.
If a gallstone blocks the opening of the gallbladder, the gallbladder can become infected causing fevers and constant pain. When the gallbladder is infected, it is called cholecystitis. Gallstones can also leave the gallbladder and block the bile ducts coming from the gallbladder. This can cause yellowing of the skin and eyes, an infection of the bile ducts or inflammation of the pancreas.
If there are stones in the bile duct, some people need a procedure to remove the stones from the bile duct. When people have symptoms from gallstones, this usually gets worse over time. Most of the time someone has symptoms from gallstones, an operation is the best treatment. Gallbladder removal is one of the most common operations performed by general surgeons. During this operation, the whole gallbladder is removed, not just the stones.
Common Symptoms
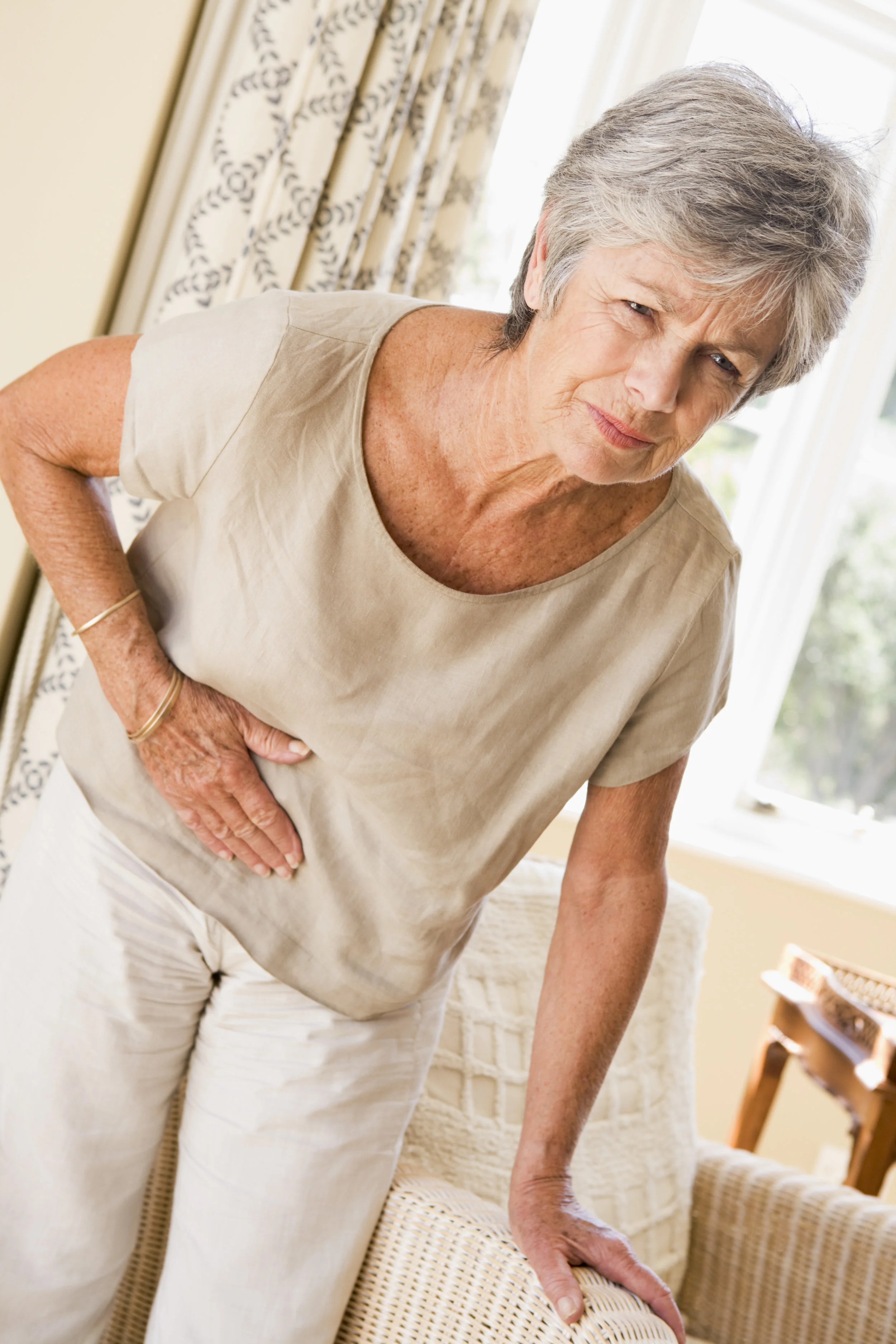
Pain in the right or middle abdomen, back or shoulders is common. Nausea, fever, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) or pain after eating can also be symptoms of gallbladder problems.
Common tests
Prior to a gallbladder operation, you will likely need blood tests and imaging studies. Some of the common imaging studies are abdominal ultrasound, hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Different tests are needed for different gallbladder problems. We will help you get the tests you need after your office visit.
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
This is the most common technique to remove the gallbladder. The surgeon makes a few small incisions in the abdomen. A lighted camera and surgical tools are placed through ports in the incision sites. The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide to make it possible to see in the internal organs. The gallbladder is removed and the incisions are closed with sutures and surgical glue. The surgeon may start with a laparoscopic technique and need to change to the open laparotomy technique. The procedure usually takes about an hour. Most people go home the same day of the operation.
Open Cholecystectomy
This is also known as the open laparotomy technique. The surgeon makes an incision about 6 inches long in the upper right side of the abdomen through the muscles to get to the gallbladder. The gallbladder is removed. The incision is stapled or sutured closed. The procedure usually takes 1-2 hours. You usually have to spend the night in the hospital after the operation for observation.